Are you battling with the problem of sudden hair loss? Learn about the signs, causes, and treatment options for alopecia areata, including the top hair fall solutions and methods to support potential revival.
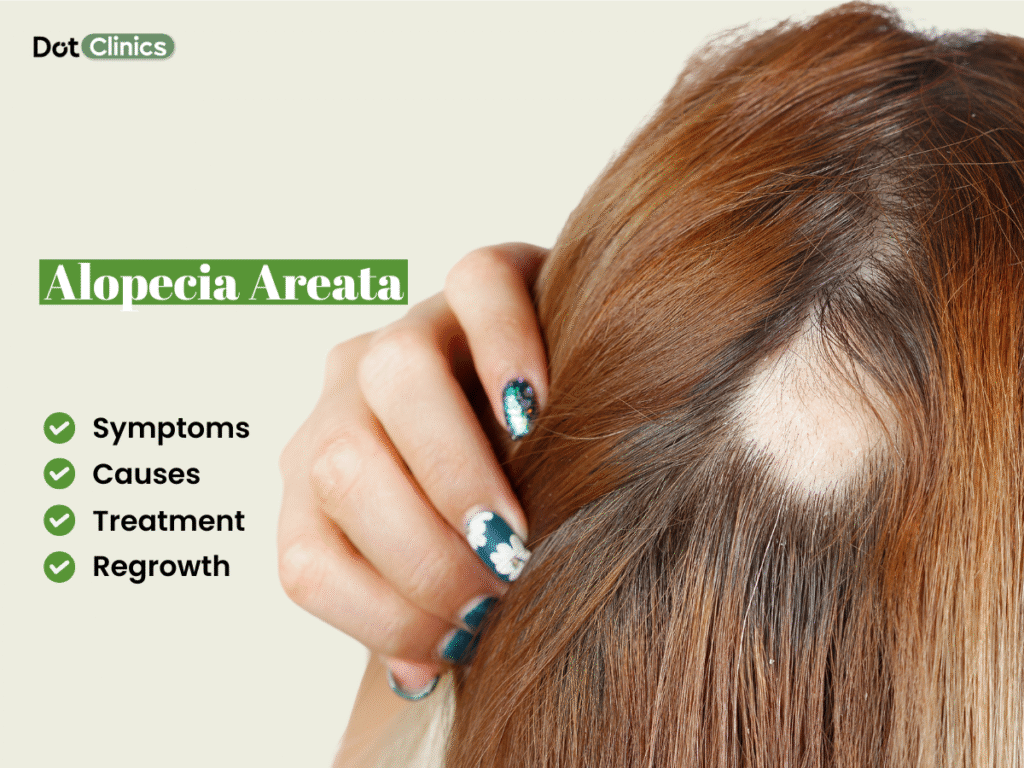
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a condition that causes sudden hair loss, initially on the scalp and if not treated then later on also affects the other hair sections of the body. This disorder occurs when the body’s defense mechanism mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing them to shrink and slow down the hair growth. Spot baldness can be distressing for many people but now many alopecia areata treatments and hair fall solutions are accessible to aid in managing and reversing hair loss.
Symptoms of alopecia areata
Symptoms can vary from person to person. Most observable signs include:
- Hair falls out in small, round patches on the scalp or other areas of the body.
- At the edge of the bald patches, short, broken hair that narrows at the base can be seen.
- Dents, ridges, or white spots on fingernails and toenails.
- Before hair loss begins, some people feel mild irritation.
Hair may regrow in certain areas and shed in others making the situation uncertain.
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of alopecia areata is not clear, but genetic and environmental factors can play a major role. Here are some contributors:
| Causes and risk factors | |
| Autoimmune response | The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles and causes shrinkage and hair loss. |
| Genetic predisposition | Chances are high if family members have alopecia areata or autoimmune disorders. |
| Chronic stress and trauma | Prolonged stress and chronic illness can weaken the immune system which worsen hair loss. |
| Hormonal changes | Pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid imbalances can lead to hair shedding. |
| Nutritional deficiencies | Lack of biotin, iron, zinc, and vitamin D depletes the hair roots. |
| Infections & viral illnesses | Certain infections over activate the defense mechanism and lead to alopecia areata. |
| Allergies | High immune sensitivity may cause inflammation in hair follicles. |
| Environmental factors | Pollutants, smoking, and harsh chemicals can trigger immune responses affecting hair. |
Diagnosis of alopecia areata
Spot baldness is diagnosed by visual examination of hair shedding patterns. Additional tests may include:
- A small sample of scalp tissue is examined to rule out other causes of hair loss.
- Blood tests are conducted to identify any underlying autoimmune condition such as lupus or thyroid disease.
- Gently pull a few hair to see how easily they fall out.
Treatment options for alopecia areata
There is no permanent solution for alopecia areata but several alopecia treatments and hair fall solutions can help in stimulating hair regrowth and manage symptoms.
- Topical treatments
- Corticosteroids
- Minoxidil (Rogaine)
- Anthralin
- Injections and oral medications
- Corticosteroid injections: These are directly injected into bald patches to promote regrowth.
- Oral immunosuppressants: Drugs like methotrexate or cyclosporine help in controlling autoimmune activity but come with potential side effects.
- JAK inhibitors: Baricitinib and ritlecitinib stimulate the hair regrowth.
- Light therapy (phototherapy)
UV light therapy combined with topical sensitizers might assist some individuals by adjusting immune activity in the scalp.
- Natural remedies and lifestyle changes
- Essential oils such as rosemary oil are effective.
- A diet rich in vitamins (biotin, vitamin D, and zinc) supports healthy hair growth.
- Yoga and walking can help reduce stress related hair loss.
Regrowth and long-term outlook
Hair regrowth process is different for everyone. Some experience full regrowth while others may have recurring episodes of hair loss. The prognosis depends on:
- Severity of the condition: The more extensive the hair loss, the harder it may be to regrow hair fully.
- Early treatment: Prompt alopecia treatment improves the chances of regrowth.
- Response to medication: Some people see good results with JAK inhibitors, corticosteroids, or PRP therapy, while others may need continuous care to manage their condition.
FAQs
- Is alopecia completely curable?
Some forms like this of sudden hair loss (spot baldness) may resolve on their own or with treatment but genetic hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) is usually managed rather than cured.
- Can alopecia be considered as hereditary?
Androgenic alopecia (pattern baldness) is hereditary while other types might not be hereditary and influenced by autoimmune or environmental factors.
- Are natural remedies alone cure alopecia?
Natural remedies are usually not sufficient alone for severe hair loss. These remedies can only support hair health.
- What causes alopecia areata?
Genes, stress, hormonal changes, and environmental factors can lead to spot baldness.
- How is alopecia areata identified?
Doctors diagnose alopecia areata by visual examination, scalp biopsy, and blood tests to check for autoimmune disorders.
- Can alopecia areata be passed to others?
Alopecia areata is not contagious. It is an autoimmune disorder and cannot be spread from person to person.
- Does alopecia areata go into remission?
Some people might experience spontaneous regrowth where hair grows back fully and does not fall out again. However, relapses can occur.