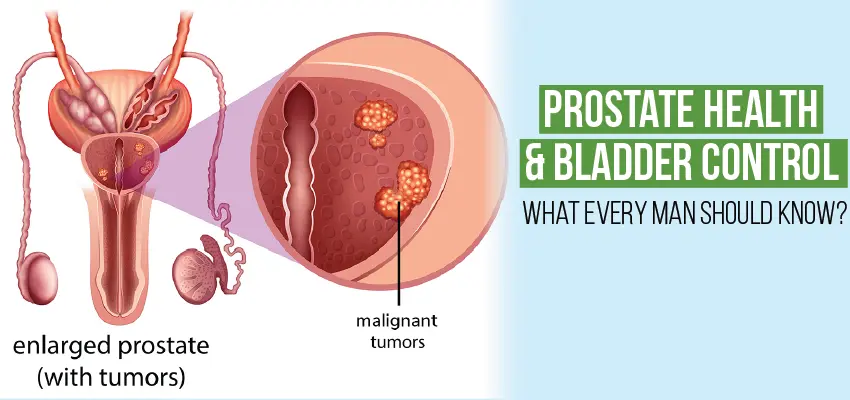
The prostate gland has a major impact on male sexual health. This condition is very common in males. Prostate cancer occurs in the prostate gland (bladder). Prostate cancer can be treated with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, brachytherapy, and hormone therapy, which are highly recommended. This disease is cured, and most people are treated without surgical treatment. Sometimes, there is no need for medication. The common types of prostate cancer are sarcomas and neuroendocrine tumours. The growth rate of prostate cancer is very slow.
What is the Prostate?
The prostate is a small gland. The prostate is about the size of a walnut. It is just present under the bladder. Or in front of the rectum. The nearby part of the urethra. This urethra produced a seminal liquid. That helps to sustain and transport the sperm. The prostate’s main function is related to sexual activity. When a male becomes old, the prostate becomes hard and may show any complications.
What is Prostate Disease?
Prostate disease is very common in males who are over 50 years old. There is no age at which this disease occurs in men. This condition shows the infection, enlargement of the prostate and prostate cancer.
Types of Prostate Disease are:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) (Size enlargement)
- Prostatitis (Inflammation/Infection)
- Prostate (Cancer)
So, given diseases have the same symptoms, but their causes are different. When your body shows any symptoms, consult with a urologist and take some screening tests.
Symptoms of Prostate Conditions:
If you notice major symptoms, never neglect them and visit a doctor’s clinic. Symptoms are given below.
- Severe pain happens in penile during ejaculation.
- Difficult to maintain an erection, called erectile dysfunction in men
- Feel pain in the pelvic area, backbone, hips, legs, arms and thighs.
- You can see visible weight loss.
- Consciously fatigue and weakness
- Blood is found in semen and urine.
- Sleep pattern disturbance. Woke up to urinate during the night
- Feel burning and sensation during urination.
- Incompletely empty bladder.
- Difficulties in controlling your urine.
- Urine colour changed to light pink, red and sometimes brown.
What are the Risk Factors and Causes of Prostate Cancer?
The most common risk factors of prostate cancer are given below.
- Age: Prostate cancer is diagnosed at the age of 50+. The prostate cancer risk increases with the passage of time and as you get older. Normally, it can happen in the 60s-70s
- Race and Ethnicity: If your grandparents and ancestry are from South Africa and America. The risks of prostate cancer increase.
- Previous Family History and DNA of Prostate Cancer: If a person has a family history of prostate cancer. The risk of cancer increases at the age of 50
- Genetically, Prostate cancer happens if this issue is genetically present from generation to generation.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: Prostate cancer is transmitted through sexual activity. But this type of cancer is transmitted rarely during or after sex.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Some chemical exposures are causing prostate cancer. A chemical was commonly used in the Vietnam War, and some industrial waste chemicals may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Smoking and Tobacco: This is the other potential factor that may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Diet and Healthy Lifestyle: Take a proper and healthy diet. Processed food and animal fats may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
How to Diagnose and Test for Prostate Cancer?
Studies recommended that infected patients talk with their health care provider about the benefits and risks of screening and testing for prostate cancer. Testing and diagnostic methods are necessary when cancer requires more detail. Some tests are given below.
Prostate-Specific-Antigen PSA Blood Test
This test helps to measure the protein in your blood. Only the prostate and prostate cancer make up the prostate cancer test. Prostate tests are usually shared in ng/mL. This is used in the treatment of cancer.
1. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
This is the physical exam used to help your urologist find a better sense of your prostate health. In this treatment, the urologist wears hand gloves and checks the prostate for lumps, hardness and enlargement of the prostate shape.
2. Prostatic MRI Method
A biopsy is used to create detailed imaging of the prostate to diagnose the suspicious and affected area.
3. Prostate Biopsy
In this method, the doctor removed a small amount of prostate tissue as a sample to examine under the microscope.
5. Initial Action Screening
Screening is normally suggested for men over 50. When you see any symptoms, share details with your doctor because prostate cancer is a slow-growing disease.
6. Follow-Up
Both prostate-specific antigen(PSA) and digital rectal exam( DRE) results show any abnormal symptoms. You must go for further tests, like an MRI and a prostate biopsy.
What are the Stages of Prostate Cancer?
The stages of prostate cancer are mainly summarised into the four main stages that can be given as a TNM system.
1. Early Stage (Stage1)
In the early stages, the tumour does not expand beyond the prostate. So this stage is also called the early stage of prostate cancer.
2. Localised Stage (Stage2)
Stage two is also called the localised stage of prostate cancer, in which the cancer has not spread outside the prostate.
3. Advanced-Loclized Stage (Stage3)
The third stage of cancer indicates that the cancerous cells spread outside the prostate and damage the nearby tissues. This is also called advanced-localised cancer.
4. Metastatic Stage (Stage4)
Cancer spreads outside the prostate as well as damages the prostate tissues and other parts like the lymph node, bones, liver and lungs. This stage is often called metastatic cancer.
What are the Treatments for Prostate Cancer?
1. Radical Prostatectomy
This is the surgical process. In which a urologist removed the entire prostate gland, tissues that are located on the sides of the prostate and seminal vesicles to treat localised prostate cancer. The purpose of removing the prostate is to cure prostate cancer.
2. Radiation Therapy
In this therapy, the high-energy rays can destroy the cancer cells. This is a very effective treatment to kill the prostate tumour.
3. Brachytherapy
This treatment is used to place the radioactive seeds inside the patient’s prostate. It helps to kill the cancerous cells while preserving the surrounding healthy tissues.
4. Hormone Therapy
Testosterone is responsible for prostate cancer growth. In this therapy, the medication blocks testosterone. Some males have had their testicles removed to prevent prostate cancer.
5. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy in prostate cancer is used as a cytotoxic drug which kills cancerous cells. It can also help to improve your quality of life. You may receive chemotherapy alone or with hormone therapy if the cancer has spread beyond your prostate.
6. Immuno Therapy
This therapy helps boost your immune system, which can kill cancer cells. It is also used in 4 stages for recurring cancer.
7. Focal Therapy
This is the latest method of prostate cancer treatment that can be used to kill the tumours which are present inside the prostate. Your doctor recommended this therapy if cancer is at low risk and has not spread further.
8. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Therapy
This type of therapy produces the powerful heat that damages the cancerous cells within your prostate.
9. Cryotherapy
However this is the newest therapy method. In which cold gases are responsible for freezing the cancerous cells in your prostate and destroying the tumour.
10. Photodynamic Therapy
Drugs make the cancerous cells more sensitive to specific wavelengths of light. The doctors expose toumar to these wavelengths of light, which eliminate the cancerous cells.
11. Laser Ablation
In laser ablation, instant heat is applied directly to the tumour; this therapy is responsible for eliminating the prostate tumour.
How to Maintain Prostate Health?
If you want your prostate stay healthy. You should adopt some healthy tips.
- Proper and Healthy Diet: Focus on a healthy diet. Eat green vegetables, fruits, and nuts, which are full of antioxidants.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise, walking and yoga, which improve hormonal health and boost blood circulation.
- Avoid Smoking: If you really want your prostate to become healthy. Avoid smoking and drinking. Both alcoholic beverages and tobacco can cause inflammation.
- Limited Red Meat: Both dairy and fatty foods, and red meat can increase the risk of prostate cancer in males.
- Limited Caffeine: Caffeine causes more urine and irritation in the prostate. So avoid excessive amounts of caffeine and other alcoholic drinks.
- Stay at a Normal Weight: Control your weight, because being overweight can be the reason for an enlarged prostate.
- Consult: If you face any kind of problem, talk to your doctor and keep regular checkups.
Conclusion:
Therefore prostate health is very important for every male. It is necessary to understand their symptoms, problems, and condition. Do you see any kind of symptoms or signs of common prostate health?
You should adopt a healthy lifestyle and go for a screening test. You must consult with your urologist and attend regular checkups.
FAQS
What are the common prostate issues?
Some common problems include BPH (enlargement), prostatitis (inflammation), and cancer.
What are the major symptoms of prostate problems?
Constant weak, burning, and pain in the urine. Blood from semen or urine, erectile dysfunction, and back pain.
Who gets prostate problems?
When a male becomes old, black men have a high risk. also genetically
Is it genetic?
Yes, family history may increase the risk of prostate problems. But not conformed.
How is prostate cancer checked?
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) and a PSA blood test are commonly used.
Does early prostate cancer show any signs?
Generally, no symptoms appear until cancer is in later stages.
What are the treatment options?
Surgery, radial and hormonal therapy, and surveillance for slow-growing cancer.
What about prostate problem side effects?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) and incontinence are common concerns with treatment.
Can we prevent prostate problems?
Yes, you can prevent disease with a healthy lifestyle, a proper diet, regular exercise, and walking.
When should I get checked?
Recommendations fluctuate by age, and risk often starts after 50. And sometimes early for high risk.